Setting up a Network between VMware Workstation Player and VirtualBox Virtual Machines
You may have faced a situation where you have virtual machines that have been set up in both VMware Workstation Player and VirtualBox (on the same computer) and would want them to communicate with one another. This would allow you, for example, to run Kali Linux (running on VMware) against a vulnerable machine such as DVWA (running on VirtualBox). In my case, most of my virtual machines have been set up in VirtualBox, whereas my Kali Linux virtual machine has been set up in VMware Workstation Player, which I used while preparing for the OSCP certification as Offensive Security only support the Kali Linux VMware image. However, with some configuration, one can set up a network between VMware Workstation Player and VirtualBox virtual machines so that the virtual machines can communicate with one other. The below steps will show you how this can be done.
Configuring VirtualBox Network Settings
- Open VirtualBox
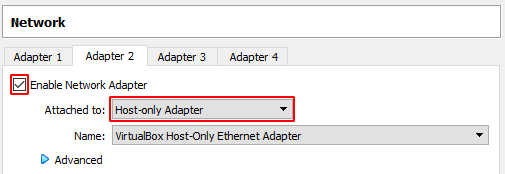
- Right-click your VM and select Settings > Network then select an unused adapter and set the network adaptor to ‘Host-only Adapter’ and click OK
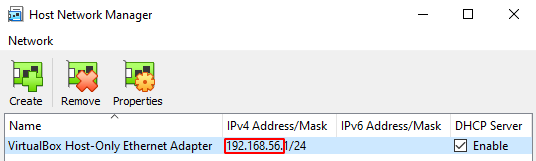
- Navigate to File > Host Network Manager, and make note of the highlighted IP address
Configuring VMware Workstation Player Network Settings
- Make sure that you have Virtual Network Editor (vmnetcfg.exe) – follow this guide on how to get it
- Run vmnetcfg.exe as administrator
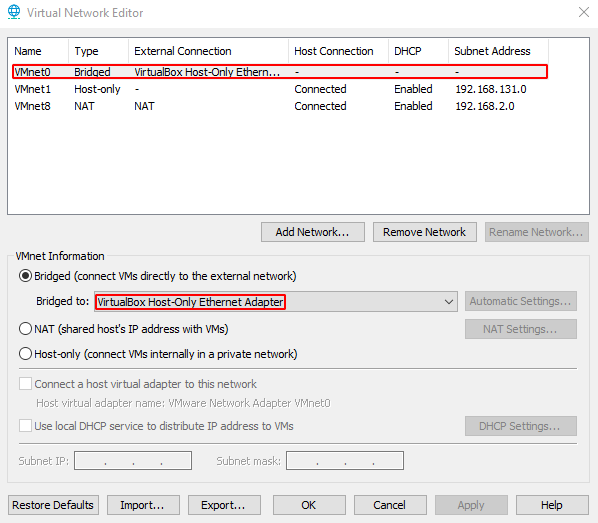
- Select ‘VMnet0’ and set ‘Bridged to’ to ‘VirtualBox Host-Only Ethernet Adapter’.
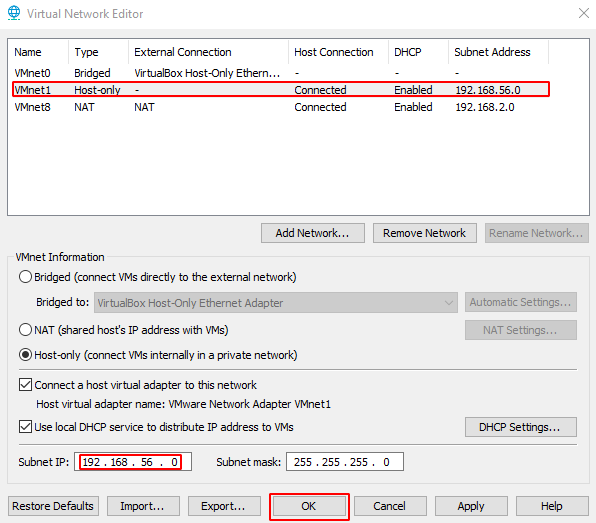
- Select ‘VMnet1’ and change the ‘Subnet IP’ to the subnet address that you obtained from Step 3 and click OK (both VirtualBox and VMWare Workstation Player virtual machines will be part of this subnet)
- Open VMware Workstation Player
- Right-click your VM and select Settings > Add > Network Adapter > Finish
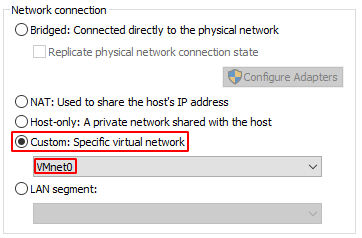
- While selecting the added adapter, change ‘Network connection’ to Custom, select ‘VMnet0’ and click OK
Verifying Network Connectivity between Virtual Machines
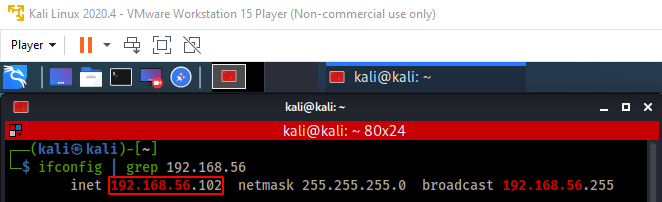
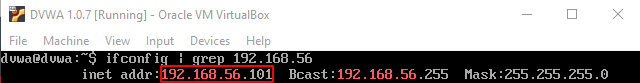
Your VirtualBox and VMWare Workstation Player virtual machines should now be able to communicate with each other. You can verify this by viewing the IP addresses of your virtual machines by running ipconfig (on Windows) or ifconfig (on Linux) from the command line. In the below screenshots, the output of ifconfig is filtered using the grep command with the subnet part of the IP address, which was configured in Virtual Network Editor.
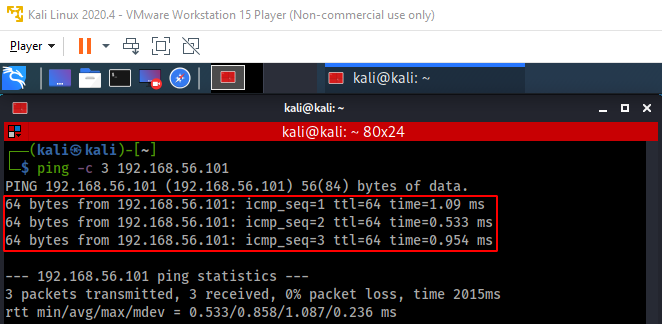
Connectivity between the virtual machines can be verified by running the ping command:
You should also be able to access other network protocols between the two virtual machines.
tags: networking virtualbox virtualization vmware